Electrode Development
|
Additives
|
|
|
Process Technology
|
|
|
Products
|
Batteries can only achieve their full potential if not only the active materials used, but also the other electrode components and their processing are taken into account. An important role is played by the inactive components that are added to improve the conductivity and mechanical properties of the electrodes. In the foreground of the investigations on electrode development are therefore binder and conductivity additives, whereby in particular their interactions with each other and the influence on the active material and the cell properties are considered. Current focus areas are the development of water-based paste systems and the determination of the additive distribution in the electrodes.
Efficient systems are available for the production of electrodes and laboratory pouch cells, which are based on industrial designs and production processes, but still allow a fast and flexible test procedure, since they are designed for a very low material usage.
Research Activities
|
Stability of Slurries Segregation effects (sedimentation, agglomeration, binder migration) are the reason for many electrode defects ► Investigation of the impact of inactive electrode components on the stability of electrode slurries. |
|
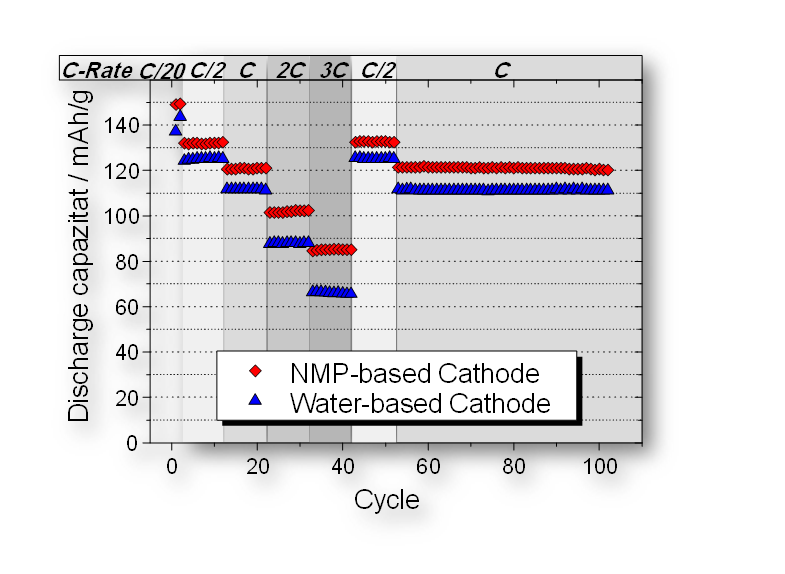 |
Aqueous Processing Usage of water as solvent is economical and ecological, but still causes processing problems and reduced cell properties ► Implementation of alternative binder systems and adaption of slurry preparation, drying and compaction process. |
|
Electrode Manufacturing Electrode manufacturing processes provide a significant contribution to the costs of the cell ► Development of improved manufacturing methods, e.g. for solvent reduced production or electrodes with enlarged thickness. |
|
|
Electrode Structure Electrode properties are strongly influenced by the local and overall distribution of electrode components ► Development of analytical methods which describe the electrode structure and enable the achievement of material - processing - property relationships. |
Electrode Manufacturing
|
|
Coating Roll-to-roll coater (KTF-S, Mathis AG) Doctor blade device Working width max. 360 mm Coating speed 0.1 to 2 m/min Two drying zones (2 x 1 m) Corona treatment |
|
|
Calendaring Batch calendar (GKL, Saueressig GmbH) |
|
|
Cell Assembling Dry room (dew point at cabin outlet <-50 °C ) Equipment for laboratory pouch cells Standard cathode size 50 x 50 mm2 Typically monolayers (capacity app. 40 mAh) Multilayer stacks feasible Manual assembling up to 30 cell/d |